Here is a discussion of community-acquired Pneumonia , regarding its routes of infection and spread, symptoms, signs , investigations and management of the disease .
Clinical Picture
• Fever , Anorexia , Headache , Malaise (toxaemia)
• Dyspnea
• Chest pain (pleurisy)
• Cough & expectoration of mucopurulant, rusty or blood stained sputum .
Palpation • Mediastinum is central, TVF II
Percussion • Dullness
Auscultation • Crepitations • Early : fine crepitation
• Late : coarse consonating crepitations
• Bronchophony Bronchial breathing ,,, Whispering pectoriloquy.
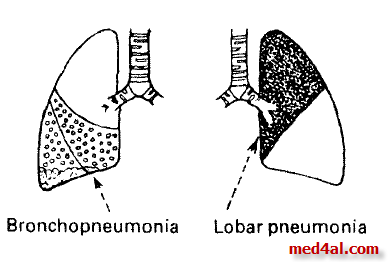
The previous signs in cases of lobar pneumonia usually are limited to one lobe of the lung, but the signs are usually bilateral and patchy and usually in lower lobes in cases
of bronchopneumonia.
2- Culture & Sensitivity for sputum.
3- Blood picture : High TLC & PNL (bacterial infection) . ESR : High
4- Blood gases showing hypoxia.
5- Serology:
• Detection of pneumococcal antigen by counter immunoelectrophoresis of sputum, urine and serum (It is more accurate than sputum or blood cultures).
• Mycoplasma antibodies IgM and IgG.
• Legionella and chylamydia antibodies.
• Legionella antigen in urine.
The duration of treatment is usually not less than 2 weeks I?
• Oral cephalosporins should not be used in the management of pneumonia as they do not penetrate well into sputum or bronchial fluids and do not cover
likey organisms.
1- Antibiotic therapy for pneumococcal and streptococcal pneumonia.
• Penicillin G injection. 1-2 gm/6hours LV.
• Erythromycin 500 mg/ 6hrs or clarithromycin (klacid) 500 mg/12hour I.V or orally
in patients allergic to penicillin.
• Ampicillin or Amoxcillin 0.5-1 mg / 6 hrs LV or orally.
2- Expectorant : K iodides.
3- Chest pain : NSAID (for pleurisy)
Cause and route of infection
Infection is usually spread by droplet inhalation and while most patients affected are previously well, cigarette smoke, alcohol and corticosteroids therapy, all impair ciliary and immune function are risk factors, other risk factors include old age, recent influenza or pre existing lung disease e.g. COPD.Clinical Picture
 symptoms :
symptoms :
• Fever , Anorexia , Headache , Malaise (toxaemia)• Dyspnea
• Chest pain (pleurisy)
• Cough & expectoration of mucopurulant, rusty or blood stained sputum .
Signs :
Inspection • Diminished movement, symmetrical chest.Palpation • Mediastinum is central, TVF II
Percussion • Dullness
Auscultation • Crepitations • Early : fine crepitation
• Late : coarse consonating crepitations
• Bronchophony Bronchial breathing ,,, Whispering pectoriloquy.
The previous signs in cases of lobar pneumonia usually are limited to one lobe of the lung, but the signs are usually bilateral and patchy and usually in lower lobes in cases
of bronchopneumonia.
Investigations to dignose Community acquired pneumonia :
1- X- ray: Homogenous opacity of a large portion of or an entire lobe of lung in case of lobar pneumonia or bilateral patchy, consolidation often affecting both lower lobes in case of bronchopneumonia.2- Culture & Sensitivity for sputum.
3- Blood picture : High TLC & PNL (bacterial infection) . ESR : High
4- Blood gases showing hypoxia.
5- Serology:
• Detection of pneumococcal antigen by counter immunoelectrophoresis of sputum, urine and serum (It is more accurate than sputum or blood cultures).
• Mycoplasma antibodies IgM and IgG.
• Legionella and chylamydia antibodies.
• Legionella antigen in urine.
Unresolving pneumonia
This means active pneumonia inspite of antibiotic therapy for 2 weeks or more :Treatment of Community acquired pneumonia :
• Generally, pneumonia is better treated with parentral antibiotics, then we start oral antibiotics when there is clinical improvement and when fever subsides.The duration of treatment is usually not less than 2 weeks I?
• Oral cephalosporins should not be used in the management of pneumonia as they do not penetrate well into sputum or bronchial fluids and do not cover
likey organisms.
1- Antibiotic therapy for pneumococcal and streptococcal pneumonia.
• Penicillin G injection. 1-2 gm/6hours LV.
• Erythromycin 500 mg/ 6hrs or clarithromycin (klacid) 500 mg/12hour I.V or orally
in patients allergic to penicillin.
• Ampicillin or Amoxcillin 0.5-1 mg / 6 hrs LV or orally.
2- Expectorant : K iodides.
3- Chest pain : NSAID (for pleurisy)
