Definition: Locally invasive, highly vascular tumor.
Incidence: 40 – 50 y. more in females.
synonyms: paraganglioma, chemodectoma.
Pathology and types of glomus tumors:
Arise from non chromafin paraganglionic cells in relation to nerves.
Glomus jugular: in relation to Arnold’s nerve on the dome of jugular bulb.
Clinical picture (symptoms and signs)
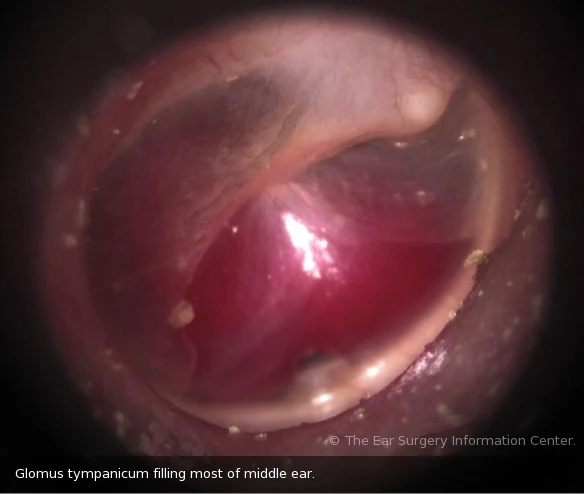
A. Otological manifestations of Glomus tumors
- Unilateral progressive deafness.
- Unilaterl pulsatile tinnitus (characteristic).
- Bloody otorrhea (Bloody ear discharge).
- Deep seated ear pain (otalgia).
- Vertigo (+ or -).
- Doctor examination: Reddish mass behind intact drum (rising sun appearance) blanches by sieglization (Brown’s sign) + Vascular polyp that bleeds on touch.
B. Cranial manifestations (Cranial nerve palsies)
- LMNL facial palsy.
- 9, 10, 11, 12 palsies in glomus jugular.
- Manifestations of increased intracranial tension (Severe headache, Projectile vomiting, Papilloedema (blurring of vision), Drowsiness and coma).
Investigations to confirm diagnosis
- CT: widening of jugular foramen, enhancing soft tissue mass destroying bone.
- Angiography: tumor blush & feeding vessels. (see figure).
- MRI, MR angiography.
- Audiogram & tympanometry.
Treatment of Glomus tumors of middle ear:
A. Surgery
Glomus tympanicum: transcanal, post. tympanotomy, radical mastoidectomy.
Glomus jugular: infratemporal fossa approach type A.
Preoperative embolization 2-3 days before surgery to decrease bleeding.
B. Inoperable cases:
Radiotherapy or embolization or both.
References
References