This article is to discuss Acute renal failure regarding definition , causes , diagnosis and treatment .
Definition :
Sudden onset of deterioration of kidney functions within a period of, days or weeks and results in uremia, it is reversible with treatment of the cause.
i. Pre-Renal ( correctable, i.e. normal kidney with low perfusion )
hemorrhage , burns , Gastroenteritis (loss of fluids ) .
Definition :
Sudden onset of deterioration of kidney functions within a period of, days or weeks and results in uremia, it is reversible with treatment of the cause.
Causes
hemorrhage , burns , Gastroenteritis (loss of fluids ) .
- Shock with normal intravascular volume .
Cardiogenic shock - Massive pulmonary embolism .
- Others
Third spacing e.g. pancreatitis, hepatorenal syndrome.
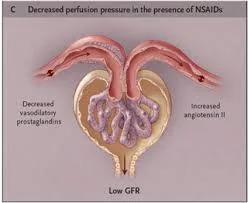
N.B Drugs that impair renal Auto-regulation e.g ACE inhibitors and NSAIDs increase liability to Pre-Renal failure .
ii . Renal causes (Intrinsic parenchymal renal disease)
• Acute tubular necrosis (ATN).
• Acute interstitial nephritis.
• Acute severe pyelonephritis >> with papillary necrosis e.g. in D.M.
• Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
• Malignant hypertension.
• Atheroembolic renal disease.
iii . Post-Renal causes ( Obstruction )
• Bilateral ureteric obstruction.
• Unilateral ureteric obstruction with non functioning or absence of the other kidney.
Clinical Picture
A. Pre-Renal
• Manifestations of the cause e.g. marked reduction of blood
pressure with oligurea, decreased skin turger, reduced
jugular venous pressure and dry mucous membranes.
B. Renal
1- Manifestations of renal failure e.g.
- Oliguria and hypertension.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Acidotic breathing.
- Weakness and arrhythmia due to hyperkalemia.
- Hypervolemia with development of pulmonary edema.
- Uraemic encephalopathy.
2- Manifestations of the cause :
- Allergic manifestations or rash in acute hypersensitivity
- interstitial nephritis.
- Puffiness in acute G.N.
- Vascular purpura in vasculitis.
- Malignant hypertension.
- Prerenal factors in ATN.
C. Post-renal
• Patients are usually less severely ill than patients with prerenal or intrinsic renal disease.
• Manifestations of the cause as renal colic, hematuria or anuria (in contrast to oliguria associated with ATN).
• Uremic manifestations may be delayed until BUN > 150 mg/dL and S. Cr > 10 mg/dL.
Investigations
** Pre-Renal
• Increased BUN and creatinine in blood.
• BUN: Cr ratio tends to be high > 20:1.
• Urine Na < 20 mmol/L.
• Urine osmolarity> 500 m.osmol/L.
• Urine analysis showing no cells or cellular casts, but few hyaline or granular casts may be present.
• Sonar is usually normal.
** Renal
• High urea and creatinine, BUN: Cr ratio is not high.
• Urine sediment is helpful e.g. RBCs, WBCs.
• Eosinophilia and eosinophiluria in hypersensitivity nephritis.
• ANCA and high ESR in vasculitis
Treatment
Treatment of Pre-Renal failure
• Treatment of the cause e.g. blood transfusion, I.V fluid therapy or treatment of heart failure.
• Central venous pressure (CVP) must be monitored to determine the rate of administration of fluids.
• Small dose dopamine may be of value to increase the renal blood flow!?
Treatment of Renal type of failure
a -General measures
- Good fluid chart.
- Control blood pressure...
- NaCH03 for acidosis.
- Low protein diet.
- Glucose/insulin for hyperkalemia.
- Domperidone for vomiting.
b -Treatment of the cause e.g.:
- Pulse steroid therapy in rapidly progressive G.N or vasculitis.
- Stop drugs causing nephrotoxicity.
- Antibiotics for sepsis or pyelonephritis.
c - Dialysis: the indications (see later).