Definition: Extension of infection from the paranasal sinuses beyond their bony walls.
Classification:
- Orbital Complication.
- Intracranial Complications: Meningitis, Epidural Abscess, Subdural Abscess, brain Abscess, and Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis.
- Bony: Osteomyelitis of Frontal Bone, mucocele, and pyocele.
Routes of Spread:
- Direct Spread through Bone or congenital dehiscence.
- Venous Spread: absence of venous valves between the orbit and sinuses facilitates retrograde venous spread of infection.
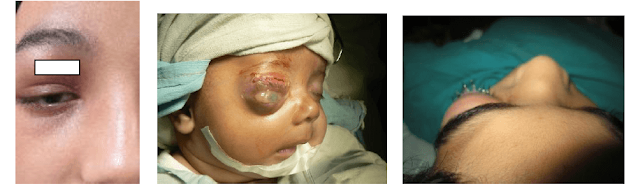
I. Orbital Complications
- Commonest complication (75%).
- It is more common in children under the age of six years (50 %).
- The ethmoid sinus is the most frequent sinus to cause orbital complications of sinusitis.
a. Orbital Edema: (Preseptal Cellulitis)
- Upper eye lid edema.
- There is NO proptosis, NO affection of vision.
- NO ophthalmoplegia.
- The lower eye lid is NOT affected.
b. Orbital Cellulitis
- Diffuse edema of the orbital content with NO pus formation.
- There is pain, chemosis, proptosis, and ophthalmoplegia (Limitation of eye movement).
- Diminution of vision, if present, is reversible.
c. Subperiosteal Abscess
- There is abscess formation deep to the periosteum of the orbital bones usually at the Lamina Papyracea.
- In addition to the above symptoms there may be: Throbbing pain, lateral Proptosis, Diminution of vision is more marked and reversible.
d. Orbital Abscess
- There is abscess formation within the orbit which has breached the periosteum.
- Symptoms are the same but more severe and diminution of vision may be Irreversible.
The inflammatory process has extended through the optic foramen into the cavernous sinus which thromboses and possibly progress to abscess formation.
Investigations:
- C.T. of paranasal sinus axial & coronal cuts with IV contrast
- Visual acuity and fundus examination.
Treatment of Complications of Sinusitis:
a. Medical:
- Hospitalization.
- Massive broad spectrum intravenous antibiotics for 10 days, for example cephalosporins plus metronidazole.
- Nasal wash and decongestant nasal drops.
- Systemic steroids: controversial.
- Strict follow up of the patient is a must with daily monitoring of visual acuity.
b. Surgical:
Indications for surgery:
- Failure of any response to medical treatment for 48 hours
- Threat to vision
- Formation of Subperiosteal or orbital Abscess.
Type of Surgery:
- ESS Complete ethmoidectomy and removal of lamina papyracea with abscess drainage.
- External Approach: rarely needed.
N.B: Orbital complication of posterior group of sinuses:
- Orbital Apex Syndrome.
- Superior orbital fissure syndrome.
- Isolated Optic Neuritis: very rare.
II. Intracranial Complications:
Look before at complications of CSOM (but here, the frontal lobe is affected which may lead to behavioral changes and memory changes).