Here are the Extra-articular manifestations of Rheumatoid arthritis, which represents the second half of the clinical picture of R.A .
1- Constitutional symptoms
• Fever.
• Weight loss.
• Easy fatigue.
2- Skin
• Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules (see before).
• Hyperhidrosis.
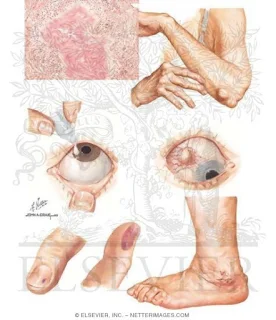 • Raynaud's phenomenon.
• Raynaud's phenomenon.
• Palmar erythema.
• Vasculitis.
3- Spleen and LNs enlargement. ( it is a feature of Felty's syndrome).
4- Eye
• Scleritis - Iritis - Episcleritis (inflammation of the superficial sclera).
• Kerato - Conjunctivitis - sicca (with sjogren's syndrome)
• Scleromalacia which is painless thining of the sclera with the affected area appearing blue (the colour of the underlying choroid).
5- Heart.
- Asymptomatic Pericarditis.
- Myocarditis.
- Aortic incompetence, pericadial effusion in 30% of patients with positive rheumatoid factor.
- Conduction defects.
- Coronary vasculitis with coronary artery occlusion.
- Endocarditis.
6- Respiratory
• Circoartenoid arthritis? hoarsness of voice.
• Pleural effusion, it is common and occurs in 30% of patients especially with positive rheumatoid factor, the effusion fluid is an exudative with high LDH and low glucose level.
• Rheumatoid pulmonary nodules do not usually cause symptoms and are detected by chest x-ray performed for other reasons.
They are multiple and subpleural. Solitary nodule can mimic bronchial carcinoma, but multiple can mimic metastatic disease.
Cavitation of nodules can raise the possibility of tuberculosis and cause pneumothorax.
• Caplan's syndrome is the combination of rheumatoid nodules and pneumoconiosis.
• Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
• Pulmonary vasculitis with pulmonary hypertension.
• Bronchiolitis.
7- Haematological features.
• Normocytic normochromic (anaemia of chronic disease).
• Iron deficiency (blood loss) due to drug induced gastritis (NSAID).
• Hypersplenism with felty's syndrome causing normocytic normochromic anaemia plus thrombocytopenia.
• Thrombocytosis with disease activity.
8- Neurological features.
• Entrapment neuropathies result from compression of peripheral nerves due to hypertrophied synovium or joint subluxation.
Median nerve compression is the most common (carpal tunnel syndrome).
• Polyneuropathy and mononeuritis multiplex may occur due to vasculitic neuropathy (vasculitis of vasa nervorum).
• Cervical cord compression can result from subluxation of the cervical spine at the atlanto axial joint. It can lead to cord compression or sudden death following minor trauma or manipulation.
Atlanto-axial subluxation should be suspected in any patient with RA who developed new onset of occipital headache, especially if symptoms of parathesia or electric shock are present in the arms .
9- Renal
• . Rheumatoid arthritis itself usu.ally doesn't lead to G.N!?
• Main cause of glomerulonephritis is drug induced : NSAIDs , Gold , Pencillamine
• Rheumatoid arthritis ~ amyloidosis kidney.
10- Vasculitis.
• A large vessel arthritis, histologically resembling P.A. N. It may lead to mesenteric, coronary, renal and cerebral artery occlusion, nail fold infarcts may also occur.
• Skin necrosis or digital gangrene (malignant rheumatoid disease).
• It occurs in anxious persons who grind their teeth at night (there is pain, clicking in one or both joints).
• It is treated by dental correction of bite.
• Low dose tricyclic antidepressant may be helpful if there is no dental abnormality.
Important links to visit :1- Constitutional symptoms
• Fever.
• Weight loss.
• Easy fatigue.
2- Skin
• Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules (see before).
• Hyperhidrosis.
 • Raynaud's phenomenon.
• Raynaud's phenomenon.• Palmar erythema.
• Vasculitis.
3- Spleen and LNs enlargement. ( it is a feature of Felty's syndrome).
4- Eye
• Scleritis - Iritis - Episcleritis (inflammation of the superficial sclera).
• Kerato - Conjunctivitis - sicca (with sjogren's syndrome)
• Scleromalacia which is painless thining of the sclera with the affected area appearing blue (the colour of the underlying choroid).
5- Heart.
- Asymptomatic Pericarditis.
- Myocarditis.
- Aortic incompetence, pericadial effusion in 30% of patients with positive rheumatoid factor.
- Conduction defects.
- Coronary vasculitis with coronary artery occlusion.
- Endocarditis.
6- Respiratory
• Circoartenoid arthritis? hoarsness of voice.
• Pleural effusion, it is common and occurs in 30% of patients especially with positive rheumatoid factor, the effusion fluid is an exudative with high LDH and low glucose level.
• Rheumatoid pulmonary nodules do not usually cause symptoms and are detected by chest x-ray performed for other reasons.
They are multiple and subpleural. Solitary nodule can mimic bronchial carcinoma, but multiple can mimic metastatic disease.
Cavitation of nodules can raise the possibility of tuberculosis and cause pneumothorax.
• Caplan's syndrome is the combination of rheumatoid nodules and pneumoconiosis.
• Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
• Pulmonary vasculitis with pulmonary hypertension.
• Bronchiolitis.
7- Haematological features.
• Normocytic normochromic (anaemia of chronic disease).
• Iron deficiency (blood loss) due to drug induced gastritis (NSAID).
• Hypersplenism with felty's syndrome causing normocytic normochromic anaemia plus thrombocytopenia.
• Thrombocytosis with disease activity.
8- Neurological features.
• Entrapment neuropathies result from compression of peripheral nerves due to hypertrophied synovium or joint subluxation.
Median nerve compression is the most common (carpal tunnel syndrome).
• Polyneuropathy and mononeuritis multiplex may occur due to vasculitic neuropathy (vasculitis of vasa nervorum).
• Cervical cord compression can result from subluxation of the cervical spine at the atlanto axial joint. It can lead to cord compression or sudden death following minor trauma or manipulation.
Atlanto-axial subluxation should be suspected in any patient with RA who developed new onset of occipital headache, especially if symptoms of parathesia or electric shock are present in the arms .
9- Renal
• . Rheumatoid arthritis itself usu.ally doesn't lead to G.N!?
• Main cause of glomerulonephritis is drug induced : NSAIDs , Gold , Pencillamine
• Rheumatoid arthritis ~ amyloidosis kidney.
10- Vasculitis.
• A large vessel arthritis, histologically resembling P.A. N. It may lead to mesenteric, coronary, renal and cerebral artery occlusion, nail fold infarcts may also occur.
• Skin necrosis or digital gangrene (malignant rheumatoid disease).
Temporo-mandibular joint syndrome
(Associated with abnormality of bite)• It occurs in anxious persons who grind their teeth at night (there is pain, clicking in one or both joints).
• It is treated by dental correction of bite.
• Low dose tricyclic antidepressant may be helpful if there is no dental abnormality.
- Rheumatoid arthritis definition,causes and pathology
- Investigations and monitoring of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Diagnostic Criteria of rheumatoid arthritis and DD from rheumatic fever
- Clinical picture of Rheumatoid arthritis , symptoms and signs
- Treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis