In this article,we are going to discuss Hypertensive Encephalopathy regarding its definition, pathology, diagnosis,differential diagnosis and management .
What is Hypertensive Encephalopathy ?
Sudden, marked elevation of blood pressure + abnormal cerebral state. i.e brain oedema, that is potentially reversible with control of blood pressure.
Pathology
Sudden and marked increase of blood pressure --> disturbance of the cerebrovascular autoregulatory mechanisms --> brain edema.
How to diagnose a case of Hypertensive Encephalopathy ?
- Very high blood pressure, headache, visual blurring, drowsiness, convulsions.
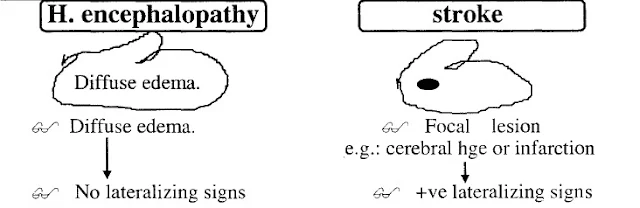
- Coma without lateralizing signs.
- Fundus examination showing papillodema and retinal hemorrhages.
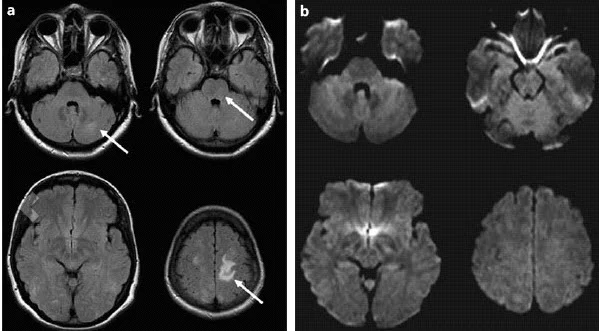
- CT and MRI show diffuse cerebral edema.
Differential diagnosis of Hypertensive Encephalopathy
It is unwise to lower the blood pressure too quickly in hypertensive enchephalopathy because this may compromise tissue perfusion due to altered autoregulatory mechanisms which can lead to cerebral damage .
Treatment of Hypertensive Encephalopathy
a. Anti hypertensive drugs :
- Glyceryl trinitrate 0.6-1.2mg/hr.
- Sodium nitroprusside 0.3-10 ug/kg/m
- Hydralazine 1.5-5 ug/kg/m.
- Labetalol 20 mg IV over 2 minutes, the dose can be doubled every 10m until control of blood pressure(maximum dose 200-300 mg).
b. For Convulsions : Diazepam IV.
c. For brain edema : Frusemide is effective .