Definition of Laryngeal stenosis:
Cicatricial narrowing of the laryngeal lumen leading to stridor.
Types of Laryngeal stenosis:
Etiology:
Congenital: Failure of canalization of endolarynx before birth.
Acquired:
- Trauma: Internal laryngeal trauma due to prolonged intubation, laryngeal surgery or radiotherapy to the neck. External trauma with fractured cricoid cartilage.
- Chronic inflammation: laryngoscleroma, T.B.
- Tumors: subglottic haemangioma or chondroma, carcinoma (vey rare 1%).
Clinical picture:
- Mild and moderete cases: no symptoms, or respiratory distress during exertion or upper respiratory infection.
- Severe cases: biphasic stridor during rest.
Examination:
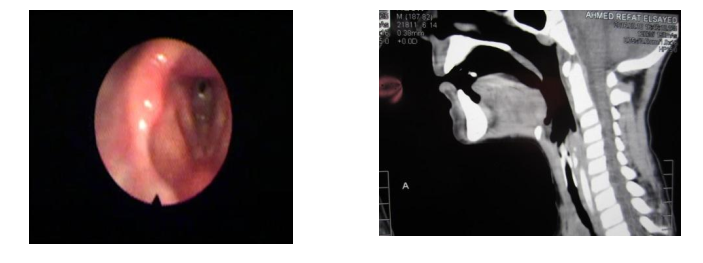
by indirect laryngoscopy or flexible larynogscopy to detect the site and degree of
narrowing.
Investigations: to detect the site, length and degree of stenosis.
- Radiological assessment as plain x-ray and CT scan
- Direct laryngoscopy under general anaesthesia.
- Pulmonary function tests pre and postoperative to evaluate prognosis.
Management:
A-Tracheostomy is lifesaving in severe cases.
B-Endoscopic procedure: Laser excision, repeated dilatation
C-External:
- Laryngoplasty: Split cricoid, Insert costal cartilage graft & put montgomery tube.
- Resection & end to end anastomosis.