I. Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy)
Definition: Collection of pus between fibrous capsule of the tonsil, usually at its upper pole &
the superior constrictor muscle.
Etiology:
- Usually as a complication of acute tonsillitis
- Organisms: usually mixed aerobic & anaerobic infection.
Incidence: Usually young adult
Pathology: Starts by infection in the depth of one of the crypts (usually crypta magna).
Symptoms:
(as tonsillitis but more severe)
General: Fever, headache, malaise (if pus >> hectic fever).
Local:
- Sore throat, severe & unilateral.
- Severe dysphagia & odynophagia.
- Unilateral neck pain & referred otalgia.
- Foetor oris
- Drooling
Signs:
Local:
- Trismus, torticollis – muffled voice
- Asymmetrical edema and congestion of soft palate.
- Swelling above & lateral to tonsil
- Tonsil is displaced downwards & medially.
- Uvula is edematous & pushed to other side.
- Large , firm , tender jugulodigastric LN.
Treatment:
A) During stage of peritonsillar cellulitis
- Parentral antibiotics
- Antipyretics , analgesics , bed rest , adequate fluids,& mouth wash
B) During stage of peritonsillar abscess
- Indicated by: Hectic fever,throbbing pain, pitting edema on probing, and aspiration of pus.
- Treated by: Incision & drainage Parentral antibiotics
Site of incision:
- Most bulging point
- Mid point of a line from base of uvula to last upper molar tooth.
- 1/2 cm lat. to point of crossing of a vertical line along anterior pillar with a horizontal line
- along base of uvula.
Technique: use a guarded knife, Hilton method to open loculation usually under G.A
C) Tonsillectomy should be done 4-6 weeks later
Differential Diagnosis:
- Neoplasm (carcinoma,lymphoma). - Acute leukaemia. – Aneurysm of ICA
- Abscess related to upper molar tooth. -Parapharyngeal swelling.
Complications:
- Laryngeal edema & stridor.
- Pyaemia & septicaemia
- Para pharyngeal abscess
II. Parapharyngeal Abscess
Definition: Collection of pus in para pharyngeal space.
Etiology:
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Tonsillitis
- Petrositis & mastoiditis
Symptoms:
like quinsy + unilateral neck swelling
Signs: Fever, tachycardia, torticollis
Becks triad:
- Swelling in lateral Pharyngeal wall pushing a normal tonsil medially.
- Tender firm external swelling on lateral side of the neck.
- Trismus.
Treatment:
As quinsy:
Hospitalization + incision & drainage by external incision along anterior border of sternomastoid.
Differential Diagnosis: All para pharyngeal swellings (salivary gland tumors neurogenic tumors, carotid aneurysm)
Complications:
- Laryngeal oedema & stridor.
- Mediastinitis.
- Thrombosis of IJV.
- Erosion of carotid artery.
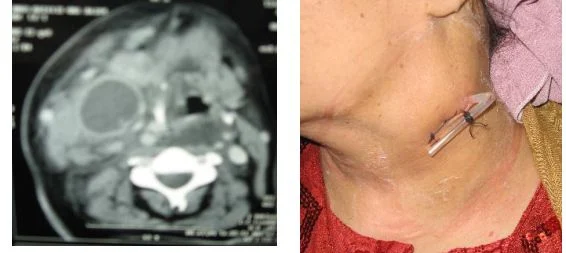
III. Retropharyngeal Abscess (R.P.A):
Collection of pus between buccopharyngeal fascia of the posterior pharyngeal wall & the
prevertebral fascia.
A) Acute R.P.A :
Etiology: Suppuration of retropharyngeal L.N (gland of Henle) following URT infection.
Incidence: Usually child, as gland atrophies later.
Pathology: Abscess occurs to one side of midline.
Symptoms:
- Fever, headache, malaise.
- Severe dysphagia.
- Stridor due to laryngeal edema
Signs:
- Fever, tachycardia, torticollis with flexed neck.
- Swelling in the posterior pharyngeal wall to one side of midline with hyperaemia &
- congestion
- Large tender cervical lymph node.
Investigations:
- Xray :widening of prevertebral space
- CT
Treatment:
- Incision & drainage: trans oral route. Head down Trendelenberg position
- Tracheostomy if stridor.
- Parentral antibiotics.
B) Chronic R.P.A ( cold abscess , Pott’s disease )
Etiology: T.B of cervical spine.
Incidence: In adult , uncommon.
Pathology: Cold abscess.
Symptoms: General: TB toxemia night fever, night sweat loss of weight, loss of appetite.
Local: Sore throat & odynophagia.
Signs:
General: Neurological signs, associated pulmonary T.B
Local: Bulge of midline of posterior pharyngeal wall and tenderness over cervical spine.
Investigation:
- Xray: destroyed vertebral bodies, chest X ray.
- Sputum analysis, tuberculin test, needle biopsy.
- CT scan
Treatment:
- Anti tuberculous treatment.
- Incision & drainage along posterior border of sternomastoid.
- Orthopedic treatment.
IV. Ludwig’s angina
Definition: Suppuration in submandibular space.
Etiology: Dental causes in 90%, infection of lower tooth, or extraction of septic tooth.
Incidence: More in diabetics.
Symptoms:
- General: Fever, headache, malaise.
- Local: Severe pain with dysphagia, muffled voice , difficult respiration .
Signs:
General: Fever, tachycardia.
Local:
Local:
- Massive indurated tender neck swelling below the mandible
- Swollen floor of mouth with the tongue pushed upwards
- Hospitalization, care of air way, toxaemia.
- Parenteral antibiotics, antipyretics, analgesics.
- Secure airway: tracheostomy.
- Drainage: a free incision decompression.