This article is to illustrate the use, significance and value of Ultrasound investigation of the the urinary system and we are focusing on Renal sonar .
(12 x 6 x3) cm
• Bipolar length (12-14 cm)
==> Shrunken
- Symmetrical : Chronic G.N.
- Asymmetrical : Chronic Pyelonephritis
==> Enlarged
- Hydronephrosis
- Amyloidosis
- Polycystic kidney
- Diabetic nephropathy
2- Stones, Tumors, Cyst .
3- Dilated pelvi-calyceal system
4- Echogenecity
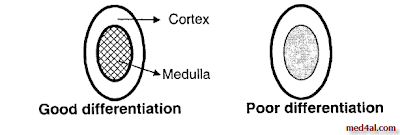
- Normally, there is a good differentiation between cortex & medulla.
- If there is poor differentiation = parenchymal disease, e.g. glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis.
5- Parenchymal Thickness
- Normally it is around 2 cm
Value and uses of kidney sonar
1- Size of the kidney(12 x 6 x3) cm
• Bipolar length (12-14 cm)
==> Shrunken
- Symmetrical : Chronic G.N.
- Asymmetrical : Chronic Pyelonephritis
==> Enlarged
- Hydronephrosis
- Amyloidosis
- Polycystic kidney
- Diabetic nephropathy
2- Stones, Tumors, Cyst .
3- Dilated pelvi-calyceal system
4- Echogenecity
- Normally, there is a good differentiation between cortex & medulla.
- If there is poor differentiation = parenchymal disease, e.g. glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis.
5- Parenchymal Thickness
- Normally it is around 2 cm
6- Biopsy guided by sonar
7- Visualization of the bladder .
- Especially bladder emptying, to assess the residual urine after micturation e.g. in cases of bladder neck obstruction, lower part ureters and prostate.