This is an approach to treatment and full management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
The disease has been discussed before in details regarding definition , causes , pathology and epidemiology and methods of diagnosis . To revise it visit HERE .
• Sunscreens and protective clothing are effective in avoiding photosensitivity reactions .
• The use of estrogen containing oral contraceptives is controversial in SLE, but many centers avoid these medications because they may increase the disease activity.
• Avoidance of vasoconstrictive drugs are helpful in treating Raynaud's phenomenon, also patients with SLE may benefit from vasodilator therapy.
• Low dose aspirin for patients with positive antiphospholipid antibodies to prevents thrombotic events .
• Psychological support is essential because SLE may cause depression and anxiety.
• Routine immunizations for influenza and pneumococci are recommended .
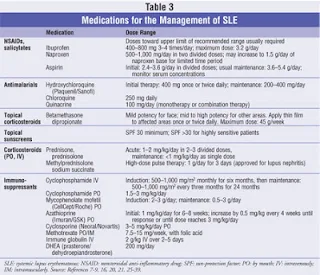
1- Arthralgia, mild arthritis, fever and serositis respond to NSAIDs .
2- Skin manifestations respond to hydroxychloroquine 400mg/d + topical steroid (hydroxychloroquine is also indicated in arthralgia resistant to
NSAIDs) .
- Steroids are used for almost all manifestations of lupus in doses ranging from extremely small alternate day doses to huge pulsed intravenous doses .
- Prolonged steroid therapy usually lead to DM , accelerated atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, glucoma, cataract, avascular necrosis and increased risk of
infections.
To avoid such toxicities, different cytotoxic drugs can be used to provide steroid sparing effect (see below).
Method
Give full dose of steroid 60-80 mg predinsolone / day till activity of the disease disappears i.e :
* Resolution of symptoms and signs.
* - ve Anti-DNA
* Normal C3 and C4
Then gradual withdrawal followed by low dose steroid as maintenance :
10-15 mg / day to prevent relapse and prevent end organ damage.
** Pulse steroid therapy can be used in severe cases (see later).
• Azathioprine (Immuran): - 2mg/kg/d orally. It is used when steroid alone is not fully effective. It is also a steroid sparing drug. i.e it allows
a reduction of steroid dose. The side effects are leucopenia, anaemia & infections.
• Cyclophosphamide (Endoxan):
1-3 mg/kg/d orally, also it can be given as pulse therapy 0.5-1 gm/m Iv.
It is important to monitor the side effects e.g Infections, bone marrow depression and infertility.
This drug is extremely toxic so, it is reserved for the most severe disease manifestations.
• Cyclosporine (Sandimmun) and mycophenolate (myfortic) can also be used with severe disease activity and to avoid the side effects of other
immunosuppressive drugs.
** Prolonged use of azathioprine may increase the risk of haematological malignancy .
5- Plasmapharesis can be used in cases with severe exacerbations refractory to steroid.
6- Immunoglobulin therapy is effective for thrombocytopenia of SLE .
Dose : 500 - 1000 mg methyl prednisolone/ day I.V. 3 - 5 days.
To be followed by full dose steroid until improvement (laboratory and clinical).
Then low dose steroid as maintenance 10 - 15 mg / day
** Pulse I.V cyclophosphamide in combination with pulse steroid is more effective.
Pulse steroid therapy can be used in SLE with severe activity. e.g. Vasculitis, cresentic GN, severe cerebral or haematological disease.
Other indications of pulse steroid therapy :
1- Cresentic glomerulonephritis (rapidly progressive G.N.)
2- Multiple sclerosis
3- Optic neuritis.
Precautions :
• Prophylaxis for peptic ulceration by proton pump inhibitors.
• Control blood pressure.
• Control blood sugar.
• Isolation to guard against infection.
• Chronic course occasionally seen.
• 5 years survival rate is about 90 %.
• Severe renal or neurological disease have the worst prognosis.
The disease has been discussed before in details regarding definition , causes , pathology and epidemiology and methods of diagnosis . To revise it visit HERE .
How to treat a patient with SLE ?
All patients require education and general prophylactic measures to prevent disease flares:• Sunscreens and protective clothing are effective in avoiding photosensitivity reactions .
• The use of estrogen containing oral contraceptives is controversial in SLE, but many centers avoid these medications because they may increase the disease activity.
• Avoidance of vasoconstrictive drugs are helpful in treating Raynaud's phenomenon, also patients with SLE may benefit from vasodilator therapy.
• Low dose aspirin for patients with positive antiphospholipid antibodies to prevents thrombotic events .
• Psychological support is essential because SLE may cause depression and anxiety.
• Routine immunizations for influenza and pneumococci are recommended .
1- Arthralgia, mild arthritis, fever and serositis respond to NSAIDs .
2- Skin manifestations respond to hydroxychloroquine 400mg/d + topical steroid (hydroxychloroquine is also indicated in arthralgia resistant to
NSAIDs) .
3- Corticosteroid therapy is the main subject of treatment.
- Steroids are used for almost all manifestations of lupus in doses ranging from extremely small alternate day doses to huge pulsed intravenous doses .
- Prolonged steroid therapy usually lead to DM , accelerated atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, glucoma, cataract, avascular necrosis and increased risk of
infections.
To avoid such toxicities, different cytotoxic drugs can be used to provide steroid sparing effect (see below).
Role of steroids
To control the inflammatory reaction --> prevent end organ damage.Method
Give full dose of steroid 60-80 mg predinsolone / day till activity of the disease disappears i.e :
* Resolution of symptoms and signs.
* - ve Anti-DNA
* Normal C3 and C4
Then gradual withdrawal followed by low dose steroid as maintenance :
10-15 mg / day to prevent relapse and prevent end organ damage.
** Pulse steroid therapy can be used in severe cases (see later).
4- Immunosuppressive drugs
Used in severe disease activity e.g severe lupus nephritis or cerebral disease.• Azathioprine (Immuran): - 2mg/kg/d orally. It is used when steroid alone is not fully effective. It is also a steroid sparing drug. i.e it allows
a reduction of steroid dose. The side effects are leucopenia, anaemia & infections.
• Cyclophosphamide (Endoxan):
1-3 mg/kg/d orally, also it can be given as pulse therapy 0.5-1 gm/m Iv.
It is important to monitor the side effects e.g Infections, bone marrow depression and infertility.
This drug is extremely toxic so, it is reserved for the most severe disease manifestations.
• Cyclosporine (Sandimmun) and mycophenolate (myfortic) can also be used with severe disease activity and to avoid the side effects of other
immunosuppressive drugs.
** Prolonged use of azathioprine may increase the risk of haematological malignancy .
5- Plasmapharesis can be used in cases with severe exacerbations refractory to steroid.
6- Immunoglobulin therapy is effective for thrombocytopenia of SLE .
Q : Pulse steroid therapy ?
Dose : 500 - 1000 mg methyl prednisolone/ day I.V. 3 - 5 days.
To be followed by full dose steroid until improvement (laboratory and clinical).
Then low dose steroid as maintenance 10 - 15 mg / day
** Pulse I.V cyclophosphamide in combination with pulse steroid is more effective.
Pulse steroid therapy can be used in SLE with severe activity. e.g. Vasculitis, cresentic GN, severe cerebral or haematological disease.
Other indications of pulse steroid therapy :
1- Cresentic glomerulonephritis (rapidly progressive G.N.)
2- Multiple sclerosis
3- Optic neuritis.
Precautions :
• Prophylaxis for peptic ulceration by proton pump inhibitors.
• Control blood pressure.
• Control blood sugar.
• Isolation to guard against infection.
Course and prognosis of SLE :
• The course is characterized by remission and exacerbation.• Chronic course occasionally seen.
• 5 years survival rate is about 90 %.
• Severe renal or neurological disease have the worst prognosis.