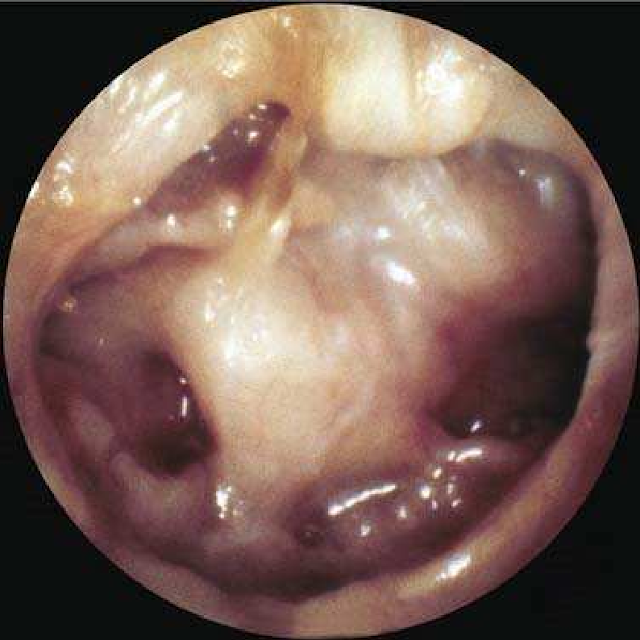
Definition: Displacement of part or all of the tympanic membrane toward the ossicles and the promontory.
Causes of Middle Ear Atelectasis
1-Prolonged Eustachian tube dysfunction or obstruction.
2-Loss of the fibrous layer of the tympanic membrane through an immune response or due to long standing middle ear effusion.
Types:
1- Localized or retraction pocket.
2- Diffuse retraction.
complications and sequelae
1-Tympanic membrane perforation.
2-Ossicular erosion.
3-Cholesteatoma formation.
Symptoms:
Deafness, or may be asymptomatic.
Signs:
Collapse of the tympanic membrane on the promontory without adhesion.
Investigations:
PTA reveals conductive hearing loss. Impedance audiometer reveals type C curve due to Eustachian tube obstruction.
Treatment of Middle Ear Atelectasis
Conservative:
It is effective in early cases. It includes exercises to ventilate the Eustachian tube as Valsalva maneuver, politzerization and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP).
Surgical:
Myringotomy with ventilation tube insertion. Cartilage tympanoplasty is indicated in severe cases.