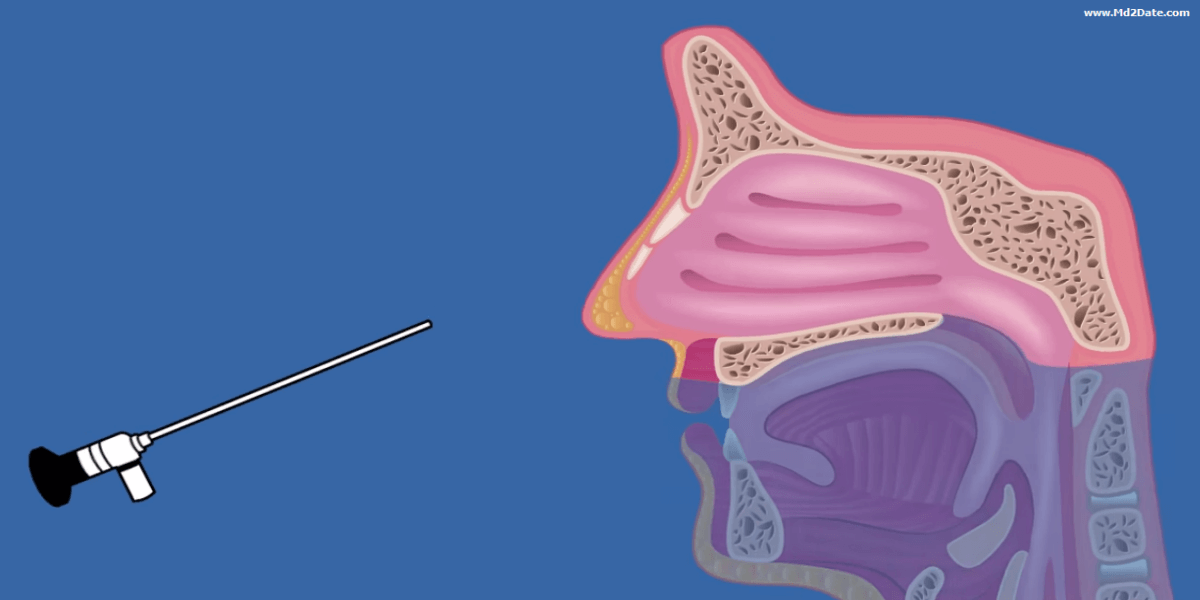
Nasal endoscopy maneuver: In the semi-sitting position. A pack (decongestant & local anesthetic) is left for 5 minutes. The endoscope is introduced via the nostril to examine the nose, sinuses and nasopharynx.
The nasal endoscopy set is composed of: Nasal endoscope, light source, cable & monitor.
Features of nasal endoscopes:
- Diameter: 2.7 mm (children) or 4 mm (adult)
- Length: 19 cm
- Angle: 0 º, 30 º, 45 ºor 70º
Indications of nasal endoscopy
I. Diagnostic:
- Choanal atresia: to confirm the diagnosis.
- Foreign body: to define site & nature of FB.
- Epistaxis: to localize site of bleeding and handle it.
- Chronic sinusitis: to visualize the pus & polyps (mainly middle meatus).
- Endoscopic guided culture & sensitivity.
- Sino-nasal polyps: to determine site & type of polyps.
- Fungal sinusitis: to visualize polyps, mud & mucin.
- Granuloma: to visualize nodules and masses.
- Sino-nasal tumor (benign and malignant): to visualize masses.
- Endoscopic guided biopsy.
- CSF leak and meningocele: to identify the meningocele and determine site of leak.
- Follow-up after ESS to achieve complete healing and to identify any residual and/or recurrence of the disease.
II. Therapeutic:
This is Endoscopic sinus surgery.
1. Basic techniques:
- Foreign body: to extract the FB safely.
- Epistaxis: to handle bleeding point/s.
- Chronic rhino-sinusitis: FESS (functional endoscopic sinus surgery)
- Mucocele: to marsupialise it.
- Sino-nasal polyps: to remove all polyps from their roots and avoid recurrence.
- Fungal rhino-sinusitis: to debride polyps, mud and mucin.
2. Advanced techniques:
- Choanal atresia: to create neochoana.
- Blow out fracture: to reduce the fracture.
- CSF leak: to repair defect.
- Meningocele: to ablate the meningocele and repair the defect.
- DCR: to create a fistula between lacrimal sac and nasal cavity.
- Benign tumors (e.g. inverted papilloma IP and juvenile angiofibroma JNA): to achieve complete resection.
- Malignant tumors: to remove early and localized lesions.
- Orbital decompression: in thyroid orbitopathy.
- Optic nerve decompression in optic neuropathy & trauma.
3. Extended techniques:
- Pituitary surgery: transnasal endoscopic pituitary surgery.
- Meningioma- chordoma- craniopharyngioma- cholesterol cyst.
- Hemangioma of orbital apex
- glioma of orbital apex
FESS in chronic rhino-sinusitis with or without polyps:
Aims of FESS:
- Preservation of the internal and external configuration of the nose.
- Removal of the source of infection
- Removal of the polyps and their roots.
- Suction of the purulent discharge.
- Insurance of the patency of the maxillary, frontal and/or sphenoid sinus ostia.
- Preservation of all the maxillary, frontal and sphenoid sinuses mucosa.
N.B. Extent of FESS is tailored according to the affected sinus/es and or side/s. All the paranasal sinuses on both sides could be taken care of as one unit in one sitting.
N.B. Diseased mucosa of the maxillary and /or frontal sinuses returns to normal after the reestablishment of proper drainage and aeration of these sinuses.
Supplementary tools during ESS:
- Shaver (microdebrider): to help shave polyps & diseased mucosa.
- Image guided surgery (navigation system): to help orientation during ESS.
Complications of ESS:
Minor: bleeding and adhesions.
Major: orbital e.g. hematoma and cranial e.g. CSF leak.
Key points
- The nasal endoscope is a tool used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- It offers excellent visualization of most of the sinonasal and nasopharyngeal cavities and recesses
- It helps achieve early and precise diagnosis
- It helps in the management of most sinonasal lesions transnasally with no need for any external incisions -ESS replaced most traditional surgeries.